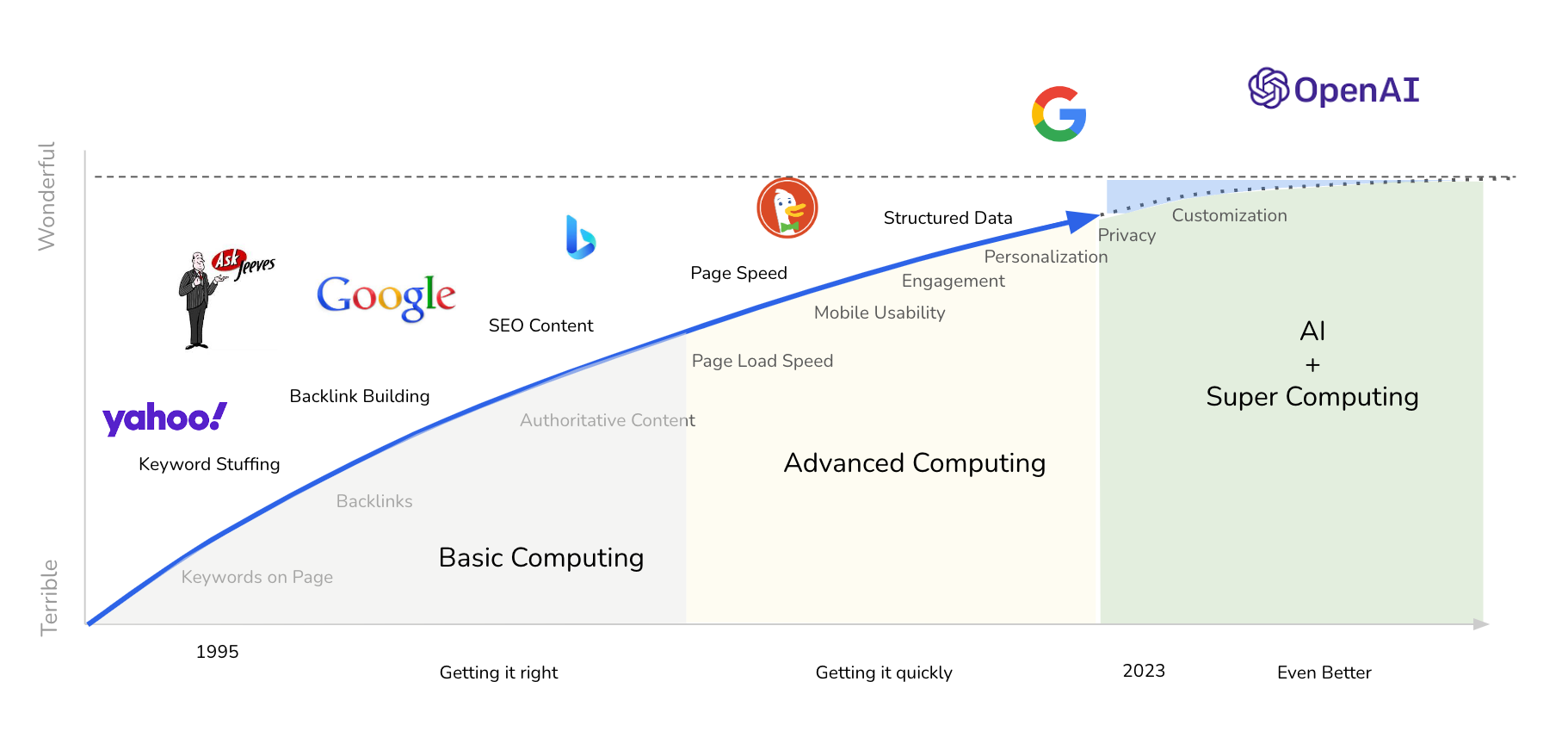
SEO is a game of economic analysis.
If you aren’t informed properly you may spend a significant amount of time and money trying to fix an SEO “issue” unnecessarily.
Avoid wasting time and money buy getting the low-down first and evaluating what impact your potential actions will have on your site.
Questions Answered Here:
- How should I manage multiple languages on my site to get the best SEO?
- How should I manage multiple regions on my site to get the best SEO?
Applicable When: you offer different content based on a visitor’s:
- Language
- Geography: Country or Region
Risk Factors
Duplicate Content – Google initiated a penalty for duplicate content when it became a popular tactic to manipulate search results back in the 90’s.
Severity: Low. Google knows how to handle accidental duplicate content created by multiple language / region sites very well by now.
Competitive Advantage Factors
Medium: If you are able to provide your specific target audience a better experience by making your content custom to their needs (region or language), you can gain an advantage over others who are just serving up generic content translated to different langauges.
When To Take Extra Care
Straight from Google’s help center. Scenarios to watch out for:
- If you keep the main content in a single language and translate only the template, such as the navigation and footer. Pages that feature user-generated content, like forums, typically do this.
- If your content has small regional variations with similar content, in a single language. For example, you might have English-language content targeted to the US, GB, and Ireland.
- If your site content is fully translated into multiple languages. For example, you have both German and English versions of each page.
What To Do To Avoid Confusion
Scenario: I Have Different Content
If…. your site(s) or pages for different languages or regions have unique content (not just a translated copy of your primary language content);
Then… you are probably safe to let Google interpret it properly.
But… if you want to be extra safe you can still follow the guidelines below.
Scenario: I Have Similar Content That’s Been Translated
If… you mostly have the same content, just translated to different languages…
Then… to be safe you should follow these best practices…
Best Practices to Follow
Languages
First: Use different URLs for your different languages.
E.g.
Primary Language English: mydomain.com/best-burritos
Secondary Language Spanish:
- mydomain.com/es/best-burritos OR
- mydomain.com/es/los-mejores-burritos OR
- mydomain.com/los-mejores-burritos
Note: using the language you are targeting in the url will help you rank for those terms in search results.
Second: Use hreflang annotations to clarify different page languages. Here is Google’s hreflang guide.
E.g. <link rel=”alternate” hreflang=”lang_code“… >
Add this code to each of your pages, specifying the “language code” for that page. This makes it extra clear to Google, which language your page is in.
Third: Keep the language consistent across the page. If your article is in Spanish, also make the header and footer Spanish.
Regions (Geotargeting)
If you have different content for different regions you can have an advantage in search results by using a country-specific domain (e.g. mydomain.de).
Note: You need to consider the cost and effort to manage different sites vs the improvement in user experience (and therefore rankings).
If your content is the same as your primary language site… just translated to a different language, then follow the guidelines above.
One More Recommendation
If you have multiple pages all in different languages…
Eg.
- mydomain.com/es/los-mejores-burritos AND
- mydomain.es/los-mejores-burritos
Then use a canonical tag to tell search engines which one you would like displayed in search results.
Canonical tags look like this: <link rel=”canonical” href=”https://example.com/es/los-mejores-burritos” />
You place the canonical tag (pointing to the 1 page you want to be the primary page) on all pages that are duplicates.
Summary
Make an assessment on whether or not your content in other languages is just a translation of your primary language OR is it different content to cater to a different audience.
If you have unique content for different regions, you can gain an advantage by using country-specific domains. But, be aware of the cost to set up and manage these vs the ranking advantage you will get in those regions (small).
If you have any chance of multiple pages in different languages, use the hreflang and canonical tags to make it super clear to Google.